Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. Spectroscopic techniques are widely used for the structure elucidation of the compounds in organic chemistry.
Techniques of Spectroscopy
- Infrared (IR): use to determination of Functional group
- Ultra violet (UV): use to determination of visible spectroscopy,, degree of unsaturation.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): use to determination of type of proton
- X-rays: use to determination of structure with stereochemistry
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): use to determination of molecular mass and molecular formula.
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Mass spectroscopy is the method for determination the molecular mass and formula of the compound and also can give information about structure. It’s a destructive technique that’s why it is called spectrometry other techniques are constructive so called spectroscopy.
Following some points are the principle of MS
- Different element are uniquely identify through their mass.
- Different Compounds are uniquely identified through their masses for example CH3CH2OH Ethanol molecular weight is 46.1 and Butorphanol molecular weight 327.
Instrumentation
In mass spectrometer molecule is vaporized and ionized by bombardment with beam of high energy electrons. When electron beam ionized the molecule then it ejects an electron. Three main function of mass spectrometer are
- Convert molecule or neutral atoms into a beam of positive or rarely negative ions.
- On the basis of mass to charge ratio ions are separated.
- Measure the relative intensity of each ion.
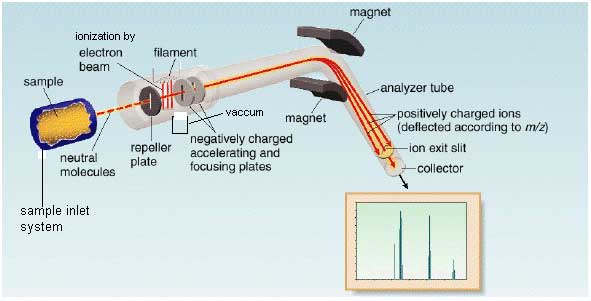
Sample inlet system
Sample we inject in ionization chamber through sample inlet system. Sample inlet system are in various forms depends upon the nature of sample. The sample may be solid liquid or gas but when sample inject it must be in vapour form.
Ionization chamber
The molecule is converted into molecular ion (M+•) in the ionization chamber by heating or bombarded with the beam of high energy electron. At the result the loss of electron from sample and formation of positive ion.
M + e– ————————-> M+•
This molecular ion is unstable that’s why it decompose and forms fragments of radicals and captions. They have lower molecular weight then molecular ion.
Filament
It is electrically heated filament which provides the high energy electron beam. For proper ionization the direction of filament is downward (perpendicular to sample molecule) toward anode.
Possible reaction in ionization chamber
- M + e –—————————–> M+ + e–
- M + e –—————————–> M– + e–
- M + e –—————————–> M + e–
- Fragments
Negative ion will be attracted by repeller plate. Accelerating plates will be attracting the positive ion.
Repeller plates
It has positive electrode potential because it attracts the negative ion.
Vacuum pump
It absorbs all neutral species.
Accelerating plates
They have negative electrode potential. They accelerate the positive ion (M+) towards analyzer from ionization chamber
Analyzer
It analyzed the sample. Then separate the positive ion according to the mass/ charge (m/e) ratio. The higher mass will move slowly then lighter mass. So there will be time difference between each ion. Every ion has different radius of curved path. Magnetic field and voltage instead of radius of curve because of radius of instrument is fixed. Every positive charge fragment pass through a curve like path towards analyzer. Every fragment has specific radius we adjust their radius according the radius of instrument by adjusting two parameter Voltage and Strength of magnetic field.
Detector
To detect the fragment it counts the ions. The fragment having same mass will reach to detector at same time.
Recorder
It records the spectrum of mass/charge ratio vs ion.
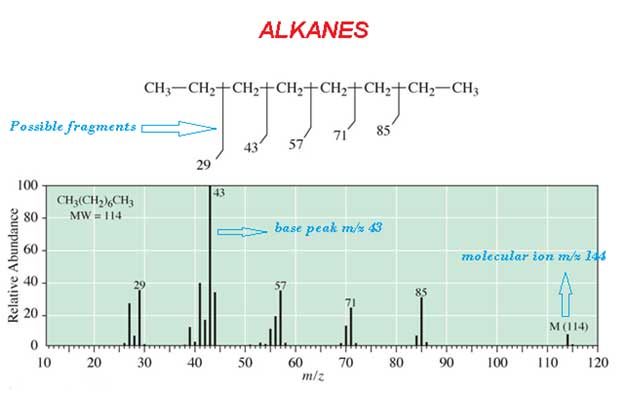
Spectrum
The most abounded peak is called base peak. For example CH3 (CH2)6 CH3 alkanes spectrum is
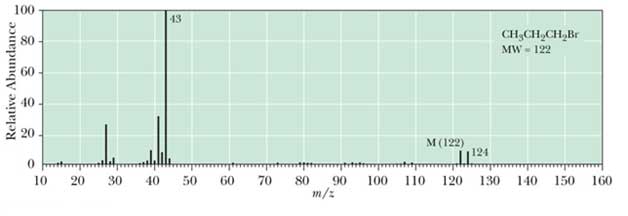
Mass Spectrometry for Isotopes
Most elements have major isotopes for example bromine. In mass spectrometry A ratio of molecule to molecular ion is 1:1 its shows a presence of a single bromine atom in compound. For example 1-bromopropane the mass spectrum is following