Here you can learn about Electronegativity of the Elements and can also download Electronegativity chart in pdf for free.
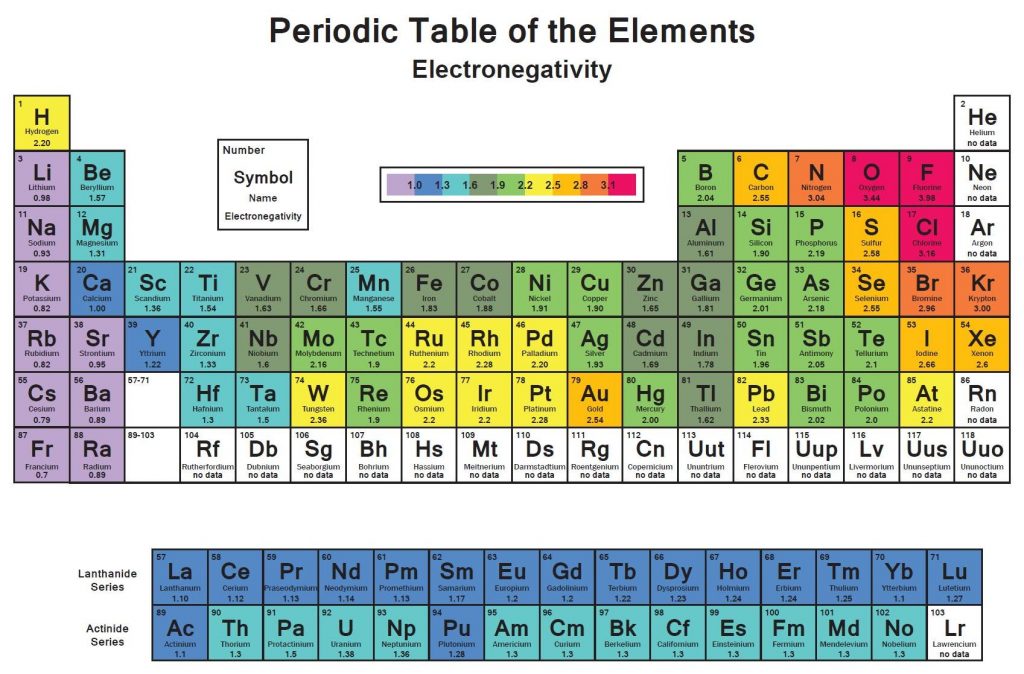
We use a quantity called electronegativity to estimate whether a given bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Electronegativity is defined as the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. The greater an atom’s electronegativity, the greater its ability to attract electrons to itself. The electronegativity of an atom in a molecule is related to the atom’s ionization energy and electron affinity, which are properties of isolated atoms. An atom with a very negative electron affinity and a high ionization energy both attracts electrons from other atoms and resists having its electrons attracted away; therefore it is highly electronegative.
Electronegativity values can be based on a variety of properties, not just ionization energy and electron affinity. The American chemist Linus Pauling (1901–1994) developed the first and most widely used electronegativity scale, which is based on thermochemical data. As Figure below shows, there is generally an increase in electronegativity from left to right across a period—that is, from the most metallic to the most nonmetallic elements. With some exceptions (especially in the transition metals), electronegativity decreases with increasing atomic number in a group. This is what we expect because we know that ionization energies decrease with increasing atomic number in a group and electron affinities do not change very much.
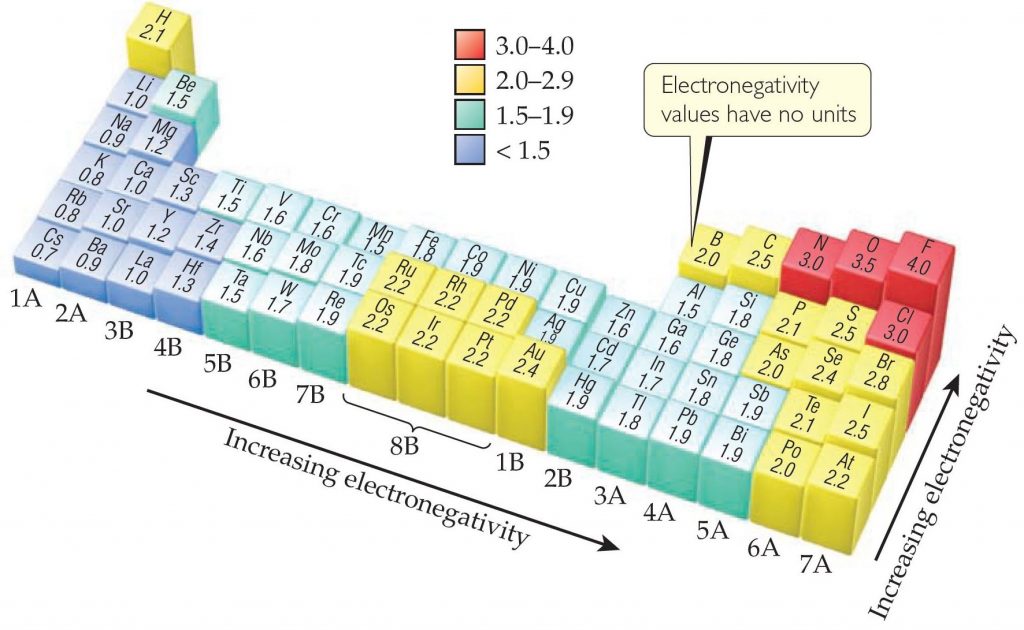
You do not need to memorize electronegativity values. Instead, you should know the periodic trends so that you can predict which of the two elements is more electronegative.
Electronegativity Chart
| NUMBER | SYMBOL | ELEMENT | ELECTRONEGATIVITY |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 2.20 |
| 2 | He | Helium | no data |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 0.98 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 1.57 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 2.04 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 2.55 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 3.04 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 3.44 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 3.98 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | no data |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 0.93 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 1.31 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum | 1.61 |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 1.90 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 2.19 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 2.58 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 3.16 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | no data |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 0.82 |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 1.00 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 1.36 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 1.54 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 1.63 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 1.66 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 1.55 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 1.83 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 1.88 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 1.91 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 1.90 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 1.65 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 1.81 |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 2.01 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 2.18 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 2.55 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 2.96 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 3.00 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 0.82 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 0.95 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 1.22 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 1.33 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 1.6 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 2.16 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | 1.9 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 2.2 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 2.28 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 2.20 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 1.93 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 1.69 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 1.78 |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 1.96 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 2.05 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 2.1 |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 2.66 |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 2.6 |
| 55 | Cs | Cesium | 0.79 |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 0.89 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 1.10 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 1.12 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 1.13 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 1.14 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | 1.13 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 1.17 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 1.2 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 1.2 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 1.22 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 1.23 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 1.24 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 1.24 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 1.25 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 1.1 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 1.27 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 1.3 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 1.5 |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 2.36 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 1.9 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 2.2 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 2.2 |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 2.28 |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 2.54 |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 2.00 |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 1.62 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 2.33 |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 2.02 |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | 2.0 |
| 85 | At | Astatine | 2.2 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | no data |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | 0.7 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | 0.89 |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | 1.1 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 1.3 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 1.5 |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 1.38 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | 1.36 |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | 1.28 |
| 95 | Am | Americium | 1.3 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | 1.3 |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | 1.3 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | 1.3 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | 1.3 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | 1.3 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | 1.3 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | 1.3 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | no data |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | no data |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | no data |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | no data |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | no data |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | no data |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | no data |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | no data |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | no data |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | no data |
| 113 | Uut | Ununtrium | no data |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | no data |
| 115 | Uup | Ununpentium | no data |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | no data |
| 117 | Uus | Ununseptium | no data |
| 118 | Uuo | Ununoctium | no data |
Download Electronegativity Chart in pdf
You can download pdf of electronegativity chart from here.
Or if you want an image of electronegativity chart you can view and download below.
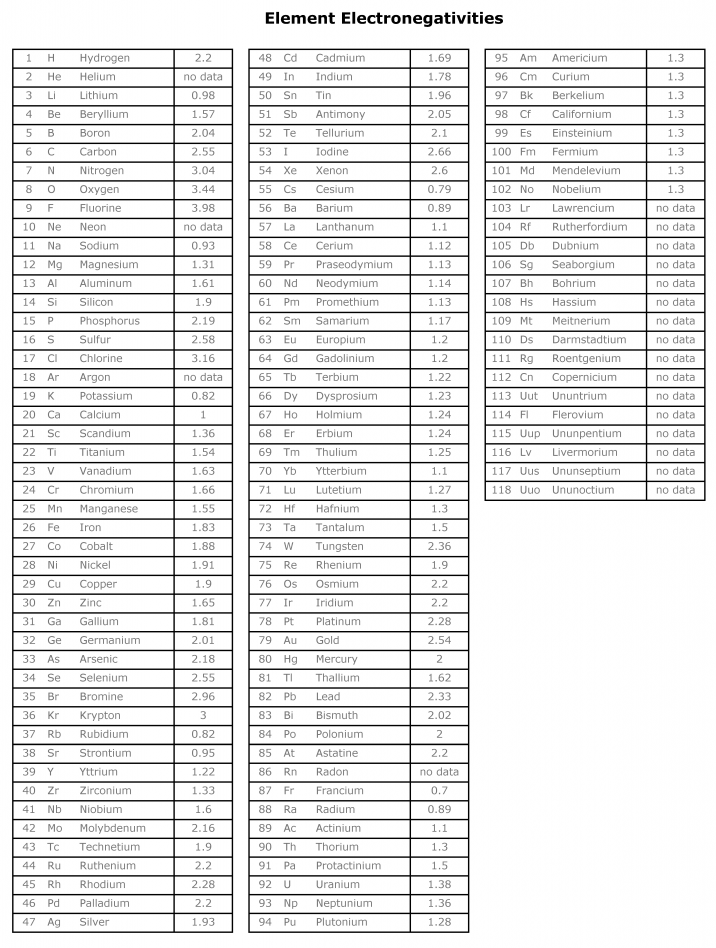 Most Electronegative Elements
Most Electronegative Elements
Here is the list of few of the most electronegative elements in periodic table.
Fluorine (F): 3.98
Oxygen (O): 3.44
Chlorine (Cl)– 3.16
Nitrogen (N)– 3.04
Bromine (Br)– 2.96
Iodine (I) – 2.66
Sulfur (S)– 2.58
Carbon (C) – 2.55
I hope you get what you are looking for. Thanks for visiting and reading.