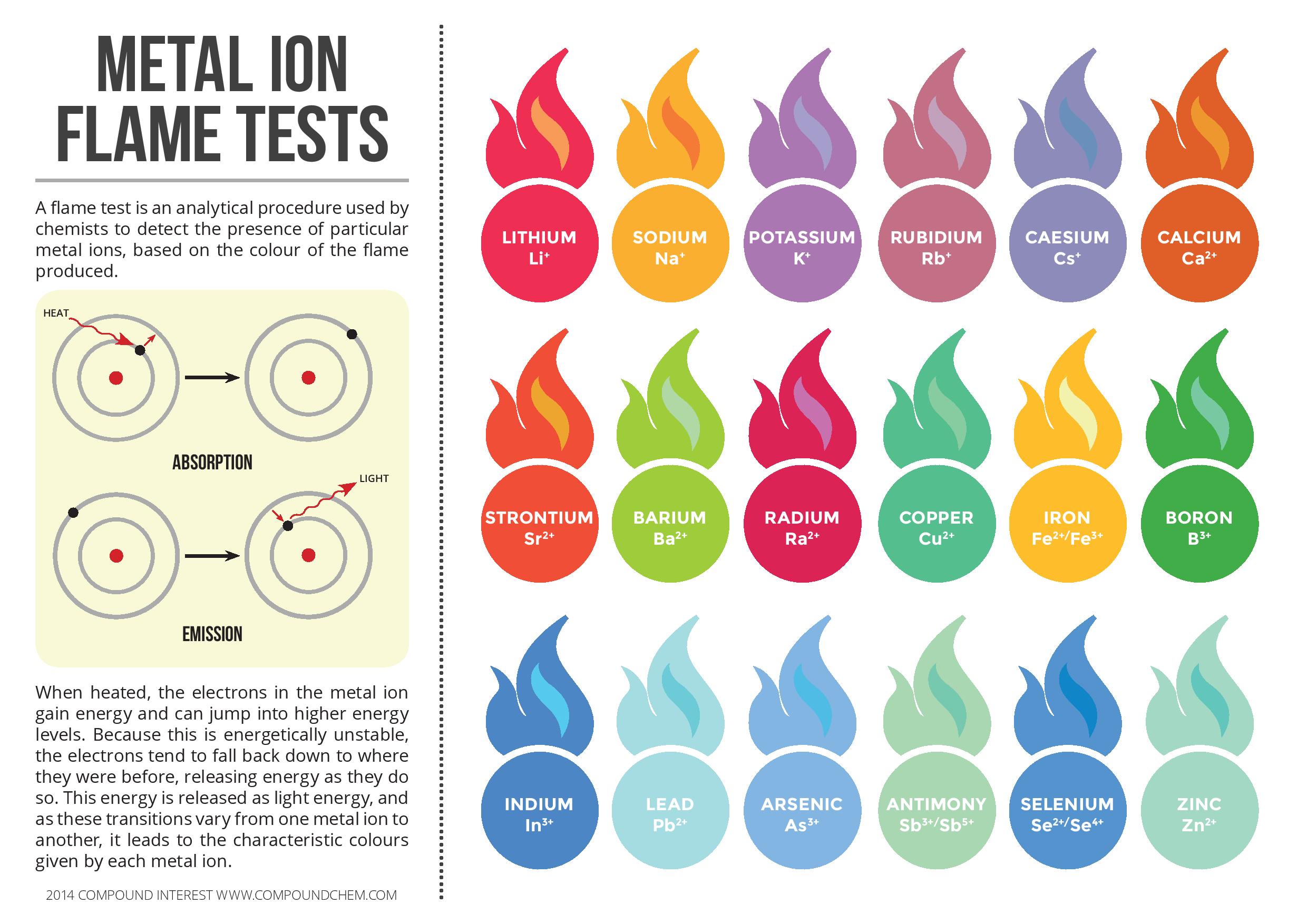
A flame test is an analytical procedure used by chemists to detect the presence of particular metal ions, based on the colour of the flame produce. When heated, the electrons in the metal ion gain energy and can jump into higher levels. Because this is energetically unstable, the electrons tend to fall back down to where they were before, releasing energy as they do so. This energy is released as a light energy, and as these transactions vary from one metal ion to another, it leads to characteristic colours given by each metal ion.
In this infographic following metal ion flame test colours described: Lithium (Li+), Sodium (Na+), Potassium (K+), Rubidium (Rb+), Caesium (Cs+), Calcium (Ca2+), Strontium (Sr2+), Barium (Ba2+), Radium (Ra2+), Copper (Cu2+), Iron (Fe2+/Fe3+), Boron (B3+), Indium (In3+), Lead (Pb2+), Arsenic (As3+), Antimony (Sb3+/Sb5+), Selenium (Se2+/Se4+) and Zinc (Zn2+).
Click to Enlarge
Read full article and download pdf of this infographic on Compound Interest.
![Colours of Transition Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution [Infographic] Colours of Transition Metal Ions](https://chemistry.com.pk/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Colours-of-Transition-Metal-Ions.png)
![Inorganic Compounds As Pigments in Paints [Infographic] Inorganic Compounds As Pigments in Paints](https://chemistry.com.pk/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Inorganic-Compounds-As-Pigments-in-Paints.png)
![The Chemistry of Fireworks [Infographic] The Chemistry of Fireworks](https://chemistry.com.pk/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/The-Chemistry-of-Fireworks.png)