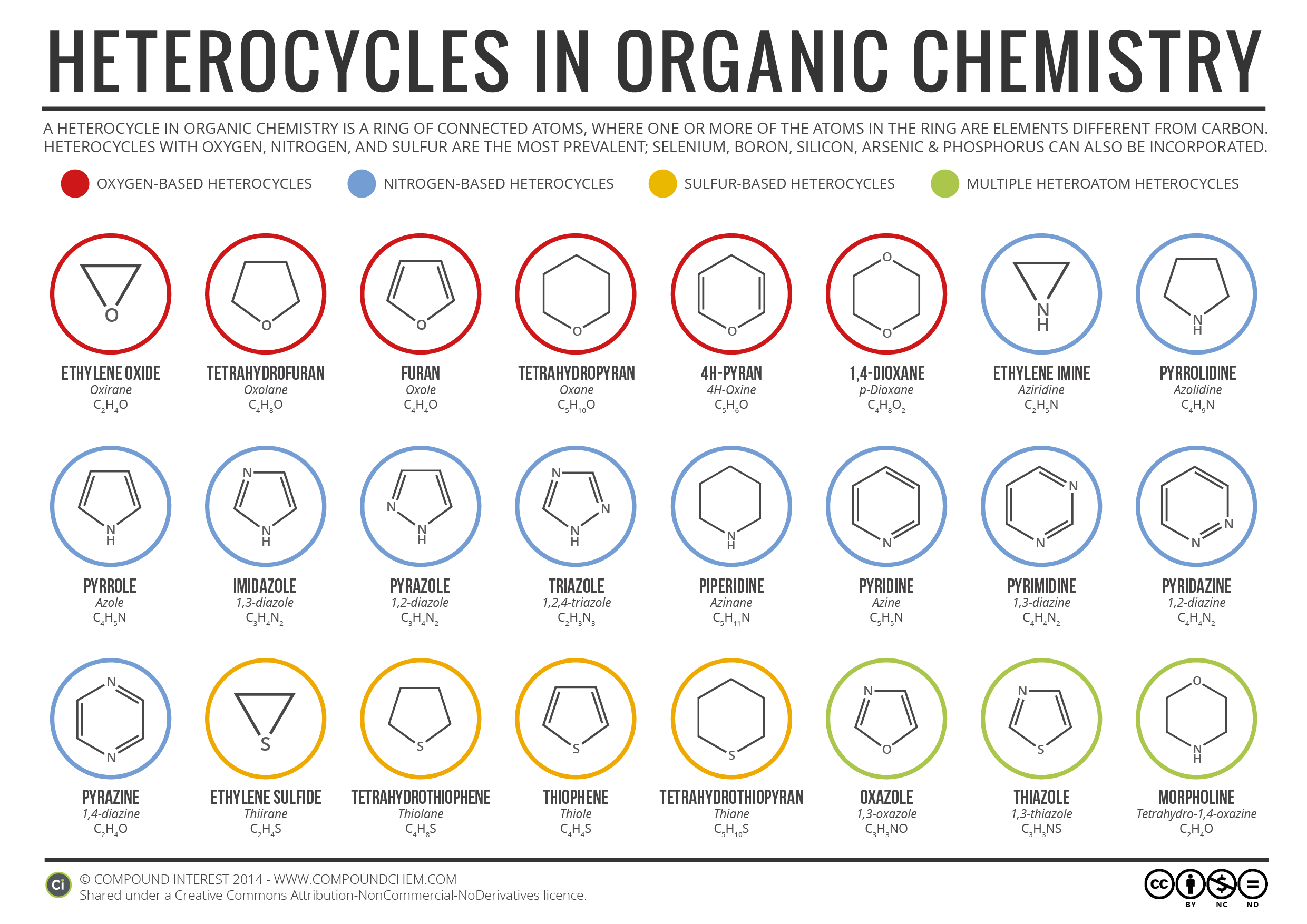
A Heterocycle in organic chemistry is a ring of connected atoms, where one or more atoms in ring are elements different from carbon. Heterocycles with Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur are the most prevalent; Selenium, Boron, Arsenic and Phosphorus can also be incorporated.
In below infographic heterocycles includes: Ethylene Oxide, Tetrahydrofuran, Furan, Tetrahydropyran, 4H-Pyran, 1,4-Dioxane, Ethylene Imine, Pyrrolidine, Pyrrole, Imidazole, Pyrazole, Triazole, Piperidine, Pyridine, Pyrimidine, Pyridazine, Pyrazine, Ethylene Sulfide, Tetrahydrothiophene, Thiophene, Tetrahydrothiopyran, Oxazole, Thiazole, Morpholine. All above heterocycles explained with their molecular and structural formulae.
click on image to enlarge
Read full article on Heterocycles in Organic Chemistry and download pdf of this infographic on Compound Interest.
![Inorganic Compounds As Pigments in Paints [Infographic] Inorganic Compounds As Pigments in Paints](https://chemistry.com.pk/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Inorganic-Compounds-As-Pigments-in-Paints.png)

![Types of Organic Chemistry Formulae [Infographic] Organic Formulae Types](https://chemistry.com.pk/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Organic-Formulae.png)